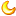|
 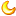
|
1#
 發表於 2011-7-5 09:17 AM
發表於 2011-7-5 09:17 AM
| 只看該作者

[貼圖] World of Deep-Sea Creatures
some very old news to share again :p
This heart-shaped jellyfish called a comb jelly was among thousands of tiny creatures captured in an expedition conducted in April to collect and catalog the world's deep-sea denizens.
The 20-day mission, sponsored by the international research group Census of Marine Life, brought 28 leading marine experts from 14 countries together in the Sargasso Sea, an area of the North Atlantic near the Bermuda Triangle.
The scientists used scuba divers and highly specialized nets and trawls to collect specimens from the ocean's deepest waters, 0.6 to 3 miles (1 to 5 kilometers) below the surface.
The researchers used a special onboard DNA sequencer to analyze more than 220 organisms, and at least a dozen new species were identified.
The research trip was funded by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and organized by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution.
This tiny, iridescent marine animal, called a zooplankton, is one of a dozen new species identified by scientists during the Census of Marine Life expedition conducted April 2006. This species is a member of the shrimplike copepods, which are among the most abundant creatures on Earth and a vital food source for many fish and marine mammals, including whales.
Census of Marine Life sponsored the mission as part of its Census of Marine Zooplankton initiative, a ten-year study begun in 2000 to inventory the biodiversity of the world's oceans.
The group plans to use the data it collects to assess the long-term effects of global warming, pollution, and ocean acidification on zooplankton, the critical first link in the ocean food chain.
This tiny sea snail, or pteropod, curiously resembles a Roman soldier's helmet. The specimen was brought up from the deep sea during last month's Census of Marine Life mission, conducted near the Bermuda Triangle.
Because most sea life exists in the ocean's upper levels, few studies until now have focused on the region below 1,000 meters (3,281 feet). But scientists believe the deeper ecosystems may play a particularly crucial role in regulating the global climate.
This tiny deep-sea snail called Atlanta peroni may be a bellwether of global warming.
Increased levels of carbon in the atmosphere, caused by burning fossil fuels among other things, is known to elevate the acidity of deep ocean water. This spike in acid levels in turn inhibits snails from growing shells.
The Earth's oceans and other bodies of water act as enormous carbon sinks that help regulate the planet's climate. Surface-dwelling plankton absorb carbon from the atmosphere and are consumed by animals called zooplankton, which come to the surface to feed and then return to the depths.
This feeding cycle transports huge amounts of carbon from the atmosphere to the sea bottom, where the crushing pressure keeps it trapped.
This baby octopus was probably using its large black eyes to search for a meal when it was snared by Census of Marine Life scientists last month.
In addition to collecting zooplankton, worms, snails, and jellies, the expedition gathered over 120 fish species, including a young oarfish, a rare male anglerfish, and what may be a new species of black dragonfish. |
附件: 您所在的用戶組無法下載或查看附件
-
1
評分次數
-
When the Buying STOPS,
The Killing STOPS!! |
|